Securing IoT Devices with Zero Trust Architecture
A Complete Guide for 2025 🔐
Introduction: The IoT Security Challenge in the Zero Trust Era 🌐
The Internet of Things (IoT) revolution has transformed how businesses operate. From smart manufacturing equipment to connected healthcare devices, IoT technology drives innovation across industries. However, this connectivity explosion creates unprecedented cybersecurity challenges that traditional security models cannot address effectively.
Why Traditional Security Falls Short for IoT 🚫
Traditional perimeter-based security assumes everything inside the network is trustworthy. This approach fails spectacularly with IoT devices. Consider a smart factory with thousands of sensors, cameras, and automated systems. Each device represents a potential entry point for cybercriminals.
Recent statistics paint a sobering picture. Cyberattacks on IoT devices increased by 87% in 2024. The average cost of an IoT-related security breach reached $4.2 million. These numbers highlight why IT professionals and DevOps engineers must rethink IoT security strategies.
Enter Zero Trust Architecture ✨
Zero trust architecture (ZTA) operates on a simple principle: “Never trust, always verify.” This security model treats every device, user, and connection as potentially compromised. For IoT environments, zero trust provides the granular control and continuous monitoring necessary to secure distributed device networks.
Zero trust for IoT devices isn’t just a buzzword. It’s becoming a business necessity. Organizations implementing zero trust models report 68% fewer security incidents and 43% faster threat detection times.

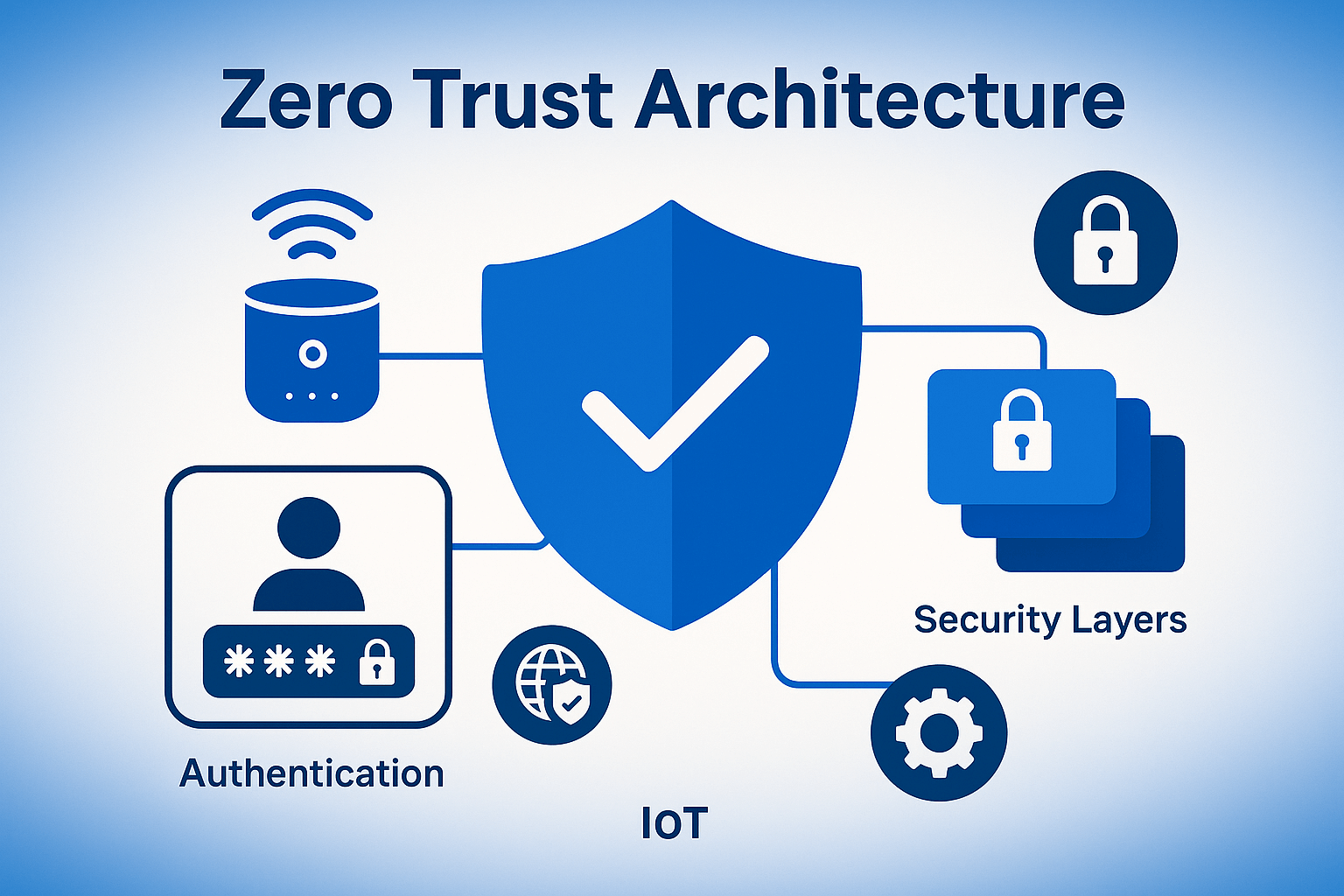
Understanding Zero Trust Model for IoT Networks 🏗️
Core Principles of Zero Trust IoT Security
Zero trust architecture rests on three fundamental pillars that reshape how we approach IoT security:
1. Explicit Verification 🔍
Every IoT device must authenticate its identity before accessing network resources. This includes device certificates, behavioral analysis, and continuous health monitoring. Unlike traditional approaches that grant broad network access, zero trust verifies each connection request individually.
2. Least Privilege Access 🎯
IoT devices receive only the minimum permissions necessary for their function. A temperature sensor doesn’t need access to financial databases. This principle dramatically reduces the potential impact of compromised devices.
3. Assume Breach ⚠️
Zero trust assumes that threats already exist within the network. This mindset drives proactive monitoring, rapid incident response, and continuous security assessment of all IoT endpoints.
Zero Trust vs Traditional IoT Security Models
| Aspect | Traditional Security | Zero Trust Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Trust Model | Trust but verify | Never trust, always verify |
| Network Access | Broad permissions | Least privilege access |
| Device Authentication | One-time verification | Continuous validation |
| Threat Detection | Perimeter-focused | Behavior-based monitoring |
| Incident Response | Reactive approach | Proactive threat hunting |
| Scalability | Limited for IoT | Designed for distributed systems |
Secure IoT Architecture with Zero Trust Implementation 🏛️
Essential Components of Zero Trust IoT Architecture
Building a secure IoT architecture with zero trust requires several interconnected components working in harmony:
Identity and Access Management (IAM) Layer 👤
Every IoT device needs a unique digital identity. This includes device certificates, authentication tokens, and identity lifecycle management. Modern IAM solutions integrate with cloud platforms like AWS IAM and Azure Active Directory to provide centralized identity governance.
Network Segmentation and Micro-Segmentation 🌐
Zero trust IoT networks implement strict segmentation. Devices are grouped based on function, risk level, and trust boundaries. Software-defined perimeters (SDP) create encrypted tunnels for device communication, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
Policy Enforcement Points (PEPs) 🛡️
PEPs act as security checkpoints throughout the IoT network. They evaluate every access request against predefined security policies. These enforcement points can be implemented through network appliances, cloud-native solutions, or software agents deployed on edge devices.
Security Orchestration and Analytics 📊
Zero trust IoT architectures generate massive amounts of security telemetry. Advanced analytics platforms, powered by AI and machine learning, process this data to identify threats, anomalies, and policy violations in real-time.
Cloud Integration for Zero Trust IoT
Modern IoT deployments leverage cloud technology for scalability and management. Major cloud providers offer specialized services:
AWS IoT Core provides device management, secure communication, and integration with other AWS services. The platform supports certificate-based authentication and fine-grained access policies.
Azure IoT Hub offers comprehensive device lifecycle management with built-in security features. Integration with Azure Security Center provides advanced threat protection for IoT deployments.
Google Cloud IoT Core focuses on data analytics and machine learning integration, enabling intelligent security responses based on device behavior patterns.
IoT Authentication and Security Layers Deep Dive 🔐
Multi-Factor Authentication for IoT Devices
IoT authentication extends beyond simple username-password combinations. Modern zero trust implementations use multiple authentication factors:
Device Certificates and PKI 📜
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) provides the foundation for IoT device authentication. Each device receives a unique certificate that serves as its digital identity. Certificate lifecycle management ensures devices maintain valid credentials throughout their operational life.
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) 🔒
HSMs provide tamper-resistant storage for cryptographic keys and certificates. These hardware components ensure that device credentials cannot be extracted or compromised, even if the device is physically accessed by attackers.
Behavioral Authentication 🎭
Zero trust systems monitor device behavior patterns to detect anomalies. Unexpected communication patterns, unusual data volumes, or unauthorized access attempts trigger additional authentication requirements or device isolation.
Security Layer Architecture
| Layer | Security Controls | Implementation Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Device Layer | Hardware security, secure boot | TPM modules, signed firmware |
| Communication Layer | Encryption, message authentication | TLS 1.3, certificate pinning |
| Application Layer | API security, data validation | OAuth 2.0, input sanitization |
| Management Layer | Policy enforcement, monitoring | SIEM integration, automated response |
IoT Security Best Practices 2025 📋
DevOps Integration for IoT Security
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) for IoT Security 🏗️
Modern DevOps practices integrate security into IoT infrastructure deployment. Terraform templates define security policies alongside infrastructure resources. This approach ensures consistent security configurations across development, testing, and production environments.
# Example: IoT device security group with zero trust principles
resource "aws_security_group" "iot_devices" {
name_description = "Zero trust security group for IoT devices"
# Restrict ingress to specific protocols and ports
ingress {
from_port = 8883
to_port = 8883
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["10.0.0.0/16"] # Internal network only
}
}Continuous Security Testing 🔍
DevOps pipelines incorporate security testing for IoT applications. Automated vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and compliance checks ensure devices meet security standards before deployment.
GitOps for IoT Security Management 📝
GitOps principles apply to IoT security configuration management. Security policies, device configurations, and access rules are stored in version-controlled repositories. Changes go through review processes before deployment, ensuring security governance and compliance.
Automation in IoT Security Operations
AI-Powered Threat Detection 🤖
Machine learning algorithms analyze IoT device behavior to identify security threats. These systems learn normal operational patterns and flag deviations that could indicate compromise or malfunction.
Automated Incident Response ⚡
Zero trust IoT architectures implement automated response capabilities. When threats are detected, systems can automatically isolate affected devices, update security policies, or initiate remediation procedures without human intervention.
Security Orchestration Workflows 🔄
Security orchestration platforms coordinate responses across multiple security tools and systems. These workflows ensure consistent, rapid responses to IoT security incidents while maintaining detailed audit trails for compliance.
Case Study: Manufacturing IoT Zero Trust Implementation 🏭
Scenario Overview
TechCorp Manufacturing operates a smart factory with 5,000+ IoT devices including sensors, robots, and monitoring equipment. Their traditional network security couldn’t handle the scale and complexity of modern IoT threats.
Implementation Architecture
┌─────────────────┐ ┌──────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ IoT Devices │────│ Zero Trust │────│ Cloud │
│ │ │ Gateway │ │ Services │
│ • Sensors │ │ │ │ │
│ • Robots │ │ • Authentication │ │ • AWS IoT Core │
│ • Cameras │ │ • Authorization │ │ • Analytics │
│ • Controllers │ │ • Encryption │ │ • AI/ML │
└─────────────────┘ └──────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘Phase 1: Device Identity Management
- Deployed PKI infrastructure for device certificates
- Implemented hardware security modules on critical devices
- Created device identity lifecycle management processes
Phase 2: Network Segmentation
- Established micro-segments based on device function
- Implemented software-defined perimeters
- Created secure communication channels between segments
Phase 3: Continuous Monitoring
- Deployed AI-powered behavioral analysis
- Integrated with SIEM systems for centralized monitoring
- Established automated threat response procedures
Results and Benefits
The implementation delivered significant security improvements:
- 73% reduction in security incidents
- 85% faster threat detection and response
- 92% improvement in compliance audit scores
- 60% reduction in security management overhead
Troubleshooting Guide: Common Zero Trust IoT Issues 🛠️
Device Authentication Problems
Issue: Certificate Expiration
Symptoms: Devices losing network connectivity, authentication failures
Solution: Implement automated certificate renewal processes, set up expiration monitoring alerts
Issue: Clock Synchronization
Symptoms: Certificate validation failures, time-based authentication errors
Solution: Deploy NTP services, configure device time synchronization policies
Network Connectivity Issues
Issue: Policy Conflicts
Symptoms: Legitimate device traffic blocked, intermittent connectivity
Solution: Review security policies for conflicts, implement policy testing environments
Issue: Performance Degradation
Symptoms: Slow device responses, increased latency
Solution: Optimize policy enforcement points, implement edge computing solutions
Why choose Devolity
Unmatched Expertise in
Cloud and Cybersecurity
Devolity team of certified professionals brings decades of combined experience in managing complex cloud environments and defending against evolving cyber threats.
01
End-to-End Solutions for Every Business Need
DevOps with Cybersecurity Services: Hybrid/multi-cloud management, cost optimization, and DevOps integration with Risk assessments.
02
Customized Strategies, Not One-Size-Fits-All
We understand every business is unique. Devolity prioritizes collaboration, crafting bespoke solutions aligned with your industry, goals, and risk profile.
03
Proactive Protection with 24/7 Vigilance
Cyber threats never sleep—and neither do we. Devolity Security Operations Center (SOC) offers round-the-clock monitoring, rapid incident response.
Monitoring and Analytics Challenges
Issue: Alert Fatigue
Symptoms: Too many false positives, delayed incident response
Solution: Tune AI models, implement risk-based alerting, create alert prioritization rules
Issue: Data Correlation Problems
Symptoms: Missed threats, incomplete incident investigation
Solution: Standardize log formats, implement data normalization, enhance correlation rules
How Devolity Optimizes Your IoT Security Journey 🚀
Devolity brings extensive expertise in cloud technology, DevOps, and cybersecurity to help organizations implement robust zero trust IoT architectures. Our team of certified professionals combines deep technical knowledge with practical implementation experience.
Our Expertise and Certifications
Our DevOps engineers hold premier certifications including AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Azure Solutions Architect Expert, and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP). This expertise ensures your IoT security implementation follows industry best practices and compliance requirements.
Comprehensive Solutions Portfolio
Cloud-Native IoT Security ☁️
We design and implement IoT security solutions leveraging AWS IoT, Azure IoT, and Google Cloud IoT platforms. Our approach integrates seamlessly with existing cloud infrastructure while providing enhanced security capabilities.
DevOps Security Integration 🔧
Our team implements Infrastructure as Code using Terraform and other modern tools to ensure consistent, repeatable IoT security deployments. We integrate security testing into CI/CD pipelines, enabling secure DevOps practices for IoT environments.
24/7 Managed Security Services 🛡️
Devolity provides continuous monitoring and management of IoT security infrastructure. Our security operations center monitors thousands of IoT devices, providing rapid threat detection and response capabilities.
Proven Track Record
With over 500 successful IoT security implementations across industries, Devolity has established itself as a trusted partner for digital transformation initiatives. Our clients experience average security incident reductions of 70% and compliance improvement scores of 85%.
Conclusion: Embracing Zero Trust for IoT Excellence 🎯
Zero trust architecture represents the future of IoT security. As IoT deployments continue expanding, organizations must adopt security models that scale with their growth while maintaining robust protection against evolving threats.
The journey to zero trust IoT security requires careful planning, skilled implementation, and ongoing management. By partnering with experienced providers like Devolity, organizations can navigate this complexity while focusing on their core business objectives.
The investment in zero trust IoT security pays dividends through reduced security incidents, improved compliance, and enhanced operational efficiency. As we move into 2025 and beyond, zero trust will become the standard for IoT security architecture.
Ready to transform your IoT security? Contact Devolity today to begin your zero trust journey and secure your connected future.
#IoTSecurity #CyberSecurity #DevOps #CloudSecurity #AIAutomation #Terraform #AWSCloud #AzureCloud #DevOpsEngineer #ITSecurity #CloudTechnology #IoTDevices #NetworkSecurity #DigitalTransformation #TechInnovation #SecurityArchitecture #IoTAuthentication #SmartDevices #ConnectedSystems
Transform Business with Cloud
Devolity simplifies state management with automation, strong security, and detailed auditing.