The Foundation of Modern Cloud Computing and DevOps Infrastructure
Understanding Hypervisors🚀
Introduction: Why Every DevOps Engineer Needs to Master Hypervisor Technology

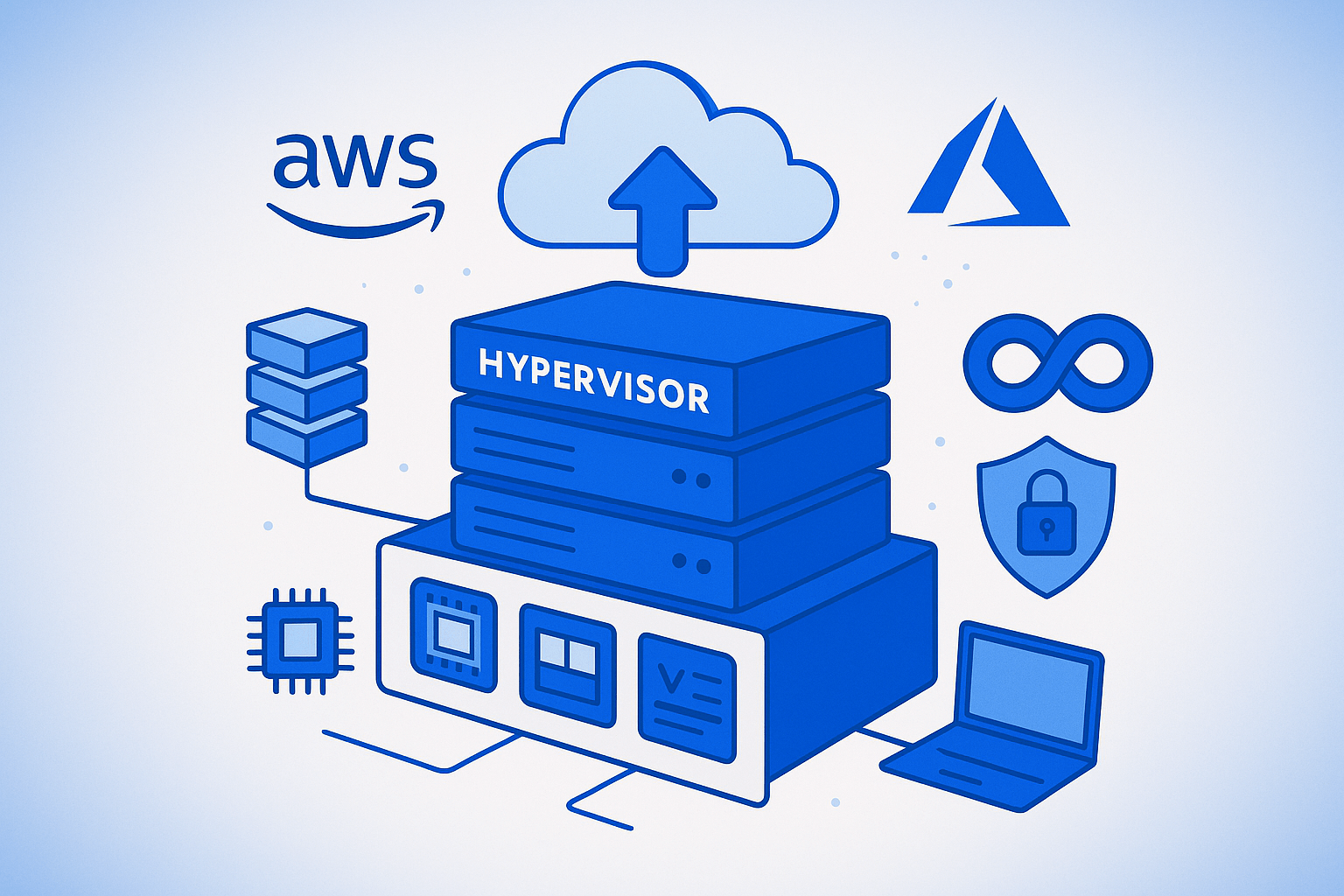
In today’s rapidly evolving cloud technology landscape, hypervisors have become the invisible backbone powering everything from AWS Cloud instances to Azure Cloud virtual machines. Whether you’re a seasoned DevOps Engineer implementing Terraform infrastructure or an IT professional securing enterprise networks, understanding hypervisor technology is no longer optional—it’s essential.
Think about it: every time you spin up a virtual machine, deploy containerized applications, or implement cyber security protocols in virtualized environments, you’re interacting with hypervisor technology. This fundamental component of modern IT infrastructure enables the automation and scalability that define today’s digital transformation initiatives.
For Devolity Hosting clients and enterprise customers alike, hypervisors represent the difference between traditional, resource-heavy IT operations and streamlined, cost-effective cloud computing solutions. But what exactly makes this technology so crucial for modern business operations?
What is a Hypervisor? The Core of Virtualization Technology
A hypervisor is essentially a software layer that creates and manages virtual machines (VMs) on physical hardware. Acting as a traffic controller for computing resources, it allocates processor power, memory, and storage to multiple virtual environments running simultaneously on a single server.
The Evolution of Hypervisor Technology
Hypervisors aren’t new technology—they’ve been around since the 1960s. Originally developed for mainframe computers, they’ve evolved dramatically with the rise of Linux and Unix systems around 2005. Today’s hypervisors power:
- AWS Cloud EC2 instances
- Microsoft Azure virtual machines
- DevOps automation pipelines
- Cyber security isolated environments
- AI and machine learning workloads
How Hypervisors Enable Modern DevOps Practices
For DevOps Engineers, hypervisors provide the foundation for:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with Terraform
- Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines
- Container orchestration platforms
- Development and testing environment isolation
- Automation of resource provisioning
Types of Hypervisors: Choosing the Right Architecture
Understanding hypervisor types is crucial for making informed infrastructure decisions. Let’s break down the two main categories:
Type 1 Hypervisors (Bare Metal/Native)
Type 1 hypervisors run directly on physical hardware, providing superior performance and security. Popular examples include:
| Hypervisor | Provider | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| VMware ESXi | VMware | Enterprise virtualization |
| Microsoft Hyper-V | Microsoft | Azure Cloud infrastructure |
| KVM | Red Hat | Open-source virtualization |
| Xen | Citrix | AWS Cloud foundation |
Benefits for DevOps Engineers:
- Higher performance for production workloads
- Better security isolation
- Direct hardware access
- Optimal for cloud technology deployments
Type 2 Hypervisors (Hosted/Embedded)
Type 2 hypervisors operate on top of existing operating systems, making them ideal for development and testing:
- VMware Workstation
- Oracle VirtualBox
- Parallels Desktop
- QEMU
Perfect for:
- Development environments
- Testing cyber security configurations
- Training and education
- Small-scale virtualization projects
Hypervisors in Cloud Computing: AWS, Azure, and Beyond
Modern cloud computing platforms rely heavily on hypervisor technology to deliver scalable, reliable services. Here’s how major providers implement virtualization:
AWS Cloud Hypervisor Implementation
Amazon Web Services uses a customized version of the Xen hypervisor called the Nitro System. This architecture provides:
- Enhanced security through hardware-based isolation
- Improved performance for AI and machine learning workloads
- Better resource utilization
- Support for DevOps automation tools
Azure Cloud Virtualization Strategy
Microsoft Azure leverages Hyper-V technology to deliver:
- Seamless integration with Windows-based environments
- Support for Linux and open-source workloads
- Cyber security features built into the hypervisor layer
- Terraform compatibility for infrastructure provisioning
Security Implications: Protecting Your Virtualized Infrastructure
Cyber security in virtualized environments requires special attention to hypervisor vulnerabilities. According to Gartner research, 35% of server virtualization vulnerabilities are hypervisor-related.
Common Hypervisor Security Threats
- VM escape attacks where malicious code breaks out of virtual machines
- Resource exhaustion attacks targeting the hypervisor layer
- Side-channel attacks exploiting shared hardware resources
- Configuration vulnerabilities in hypervisor settings
Best Practices for Hypervisor Security
- Regular updates and patch management
- Network segmentation between virtual machines
- Access control and privilege management
- Monitoring and logging of hypervisor activities
- Compliance with standards like NIST Virtualization Security Guidelines
Hypervisors in DevOps and Automation Workflows
DevOps Engineers leverage hypervisors for creating efficient, automated workflows:
Infrastructure as Code with Terraform
Terraform can provision and manage hypervisor-based infrastructure across multiple cloud providers:
resource "vsphere_virtual_machine" "vm" {
name = "terraform-test"
resource_pool_id = data.vsphere_resource_pool.pool.id
datastore_id = data.vsphere_datastore.datastore.id
}Container Orchestration and Virtualization
While containers provide application-level virtualization, they often run on hypervisor-based infrastructure, creating a layered approach to automation:
- Kubernetes clusters on virtual machines
- Docker containers within virtualized environments
- CI/CD pipelines spanning multiple virtualization layers
AI and Machine Learning on Virtualized Infrastructure
Artificial Intelligence workloads have unique requirements that modern hypervisors address:
GPU Virtualization for AI Workloads
Advanced hypervisors support GPU passthrough and vGPU technology, enabling:
- Multiple AI models running on shared hardware
- Cost-effective machine learning development environments
- Scalable training and inference pipelines
- Resource optimization for cloud technology deployments
Performance Considerations for AI Applications
- Memory allocation strategies for large datasets
- CPU scheduling optimization for ML algorithms
- Storage performance for data-intensive workloads
- Network optimization for distributed AI systems
Practical Implementation Example: Enterprise Migration to Hypervisor-Based Infrastructure
Case Study: Financial Services Company Migration
Challenge: A mid-sized financial services company needed to migrate 200+ physical servers to a virtualized environment while maintaining strict cyber security compliance.
Solution Implementation:
- Assessment Phase:
- Inventory of existing physical infrastructure
- Security requirements analysis
- Performance baseline establishment
- Architecture Design:
- Type 1 hypervisor selection (VMware vSphere)
- Network segmentation planning
- Disaster recovery integration
- Migration Execution:
- Phased migration approach
- DevOps automation tools for deployment
- Monitoring and validation processes
Results:
- 60% reduction in hardware costs
- 40% improvement in deployment speed
- Enhanced cyber security posture
- Streamlined DevOps workflows
Migration Architecture Diagram
[Physical Servers] → [Assessment Tools] → [Hypervisor Layer]
↓
[Virtual Machines] ← [Management Tools] ← [Resource Pool]Troubleshooting Guide: Common Hypervisor Issues
Performance Problems
Symptoms:
- Slow VM performance
- Resource contention
- Application timeouts
Solutions:
- Check resource allocation and usage
- Optimize memory and CPU settings
- Review storage performance metrics
- Implement automation for resource scaling
Security Vulnerabilities
Symptoms:
- Unauthorized access attempts
- Suspicious network traffic
- Configuration drift
Solutions:
- Apply latest security patches
- Review access controls and permissions
- Implement network segmentation
- Use cyber security monitoring tools
Networking Issues
Symptoms:
- VM connectivity problems
- Network performance degradation
- DNS resolution failures
Solutions:
- Verify virtual network configuration
- Check physical network connectivity
- Review firewall and routing rules
- Test network automation scripts

How Devolity Business Solutions Optimizes Your Hypervisor Infrastructure
Devolity brings extensive expertise in hypervisor technology and cloud computing solutions. Our team of certified DevOps Engineers and cloud technology specialists helps organizations:
Devolity Hypervisor Expertise
Certifications and Achievements:
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect professionals
- Microsoft Azure certified experts
- VMware certified professionals
- Red Hat certified engineers
- Terraform certified practitioners
Service Offerings:
- Cloud migration planning and execution
- Cyber security assessment and implementation
- DevOps pipeline optimization
- AI and machine learning infrastructure design
- 24/7 monitoring and support
Success Metrics from Devolity Implementations
- Average 50% cost reduction in infrastructure expenses
- 99.9% uptime for critical business applications
- 3x faster deployment times with automation
- Zero security incidents in managed environments
- 100% compliance with industry regulations
Future Trends: Hypervisors and Emerging Technologies
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
The convergence of AI technology with hypervisor capabilities is creating new opportunities:
- Intelligent resource allocation based on workload patterns
- Predictive maintenance for virtualized infrastructure
- Automated security response systems
- Machine learning-optimized virtual machine configurations
Edge Computing and Hypervisors
As edge computing grows, hypervisors are adapting to support:
- Lightweight virtualization for resource-constrained environments
- Distributed management across multiple locations
- Low-latency applications requiring local processing
- IoT device integration and management
Conclusion: Mastering Hypervisors for Digital Transformation Success
Hypervisor technology remains fundamental to modern IT infrastructure, enabling everything from cloud computing scalability to DevOps automation. For IT professionals and DevOps Engineers, understanding these systems isn’t just about technical knowledge—it’s about driving business value through efficient, secure, and scalable infrastructure solutions.
Whether you’re implementing Terraform infrastructure as code, securing virtualized environments with cyber security best practices, or optimizing AI workloads on cloud technology platforms, hypervisors provide the foundation for success.
The future of IT infrastructure lies in intelligent, automated, and secure virtualization—and hypervisors are at the heart of this transformation.
#CloudComputing #DevOps #CyberSecurity #Virtualization #AWS #Azure #Terraform #DevOpsEngineer #CloudTechnology #AI #Automation #DevolityHosting #ITInfrastructure #DigitalTransformation
Authoritative References and Backlinks
- NIST Virtualization Security Guidelines
- VMware vSphere Documentation
- Microsoft Hyper-V Technical Reference
- AWS Nitro System Documentation
- Red Hat KVM Virtualization
- Terraform VMware Provider
- Kubernetes Virtualization
- Gartner Hypervisor Security Research
About Devolity: Leading provider of cloud computing, DevOps automation, and cyber security solutions for enterprise clients worldwide. Specializing in AWS, Azure, and hybrid cloud implementations with certified expertise in hypervisor technology and infrastructure optimization.
Transform Business with Cloud
Devolity simplifies state management with automation, strong security, and detailed auditing.